IP address is a unique identifier of a computer on TCP/IP networks and on the internet. Every computer requires a unique IP address to be a part of the internet and the IP address is provided by the internet service providers. Every IP address consists of the 32 bits and a binary system of 0s and 1s. The binary number system consist of only two types of digits 0 and 1. It is easier for us to remember the decimal numbers rather than the binary number system such as 011001101. On a same network segment, all the IP address share the same network address.
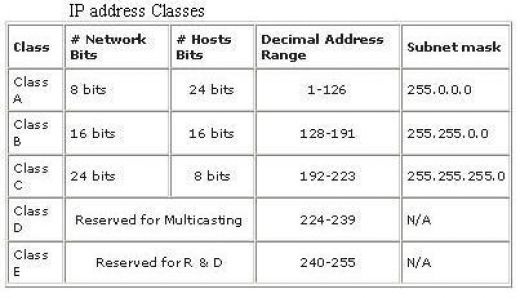
There are five classes of the IP addresses such as A, B, C, D and E and only 3 classes are in the use. Class D IP addresses are reserved for the multicast group ant cannot be assigned to hosts and the E class IP addresses are the experimental addresses and cannot be assigned to the people. Every IP address consists of 4 octets and 32 bits. Every participating host and the devices on a network such as servers, routers, switches, DNS, DHCP, gateway, web server, internet fax server and printer have their own unique addresses within the scope of the network.
TCP/IP protocols are installed by default with the Windows based operating systems. After the TCP/IP protocols are successfully installed you need to configure them through the Properties Tab of the Local Area Connection.
IP Addresses Classes
Class A
The binary address for the class A starts with 0. The range of the IP addresses in the class A is between 1 to 126 and the default subnet mask of the class A is 255.0.0.0. Class A supports 16 million hosts on each of 125 networks. An example of the class A is 10.10.1.1. Class A is used for the large networks with many network devices.
Class B
The binary address for the class B starts with 10. The range of the IP address in the class B is between 128 to 191 and the default subnet mast for the class B is 255.255.0.0. Class B supports 65,000 on each of 16,000 networks. An example of the class B address is 150.10.10.10. Class B addresses scheme is used for the medium sized networks.
Class C
The binary address for the class C starts with 110. The range of the IP addresses in the class C is between 192 to 223 and the default subnet mask for the class C is 255.255.255. Class C hosts 254 hosts on each of 2 million networks. An example of the Class C IP address is 210.100.100.50. Class C is used for the small networks with less then 256 devices and nodes in a network.
Class D
The binary addresses for the class D starts with 1110 and the IP addresses range can be between 224 to 239. An example of the class D IP address is 230.50.100.1
Class E
The binary address can starts with 1111 and the decimal can be anywhere from 240 to 255. An example of the class E IP address is 245.101.10.10
It is very important to know that all the computers in the same network segment should have the IP addresses for the same class i.e. form A, B or C
IP Addressing Tips
- A Network ID cannot be All 0s
- A host ID cannot be All 1 because this represents a broadcast address for the local network.
- Each host must have a unique host portion of the IP address.
- All hosts on the same network segment should have the same network id.
- A host address cannot be 127 because 127 has been reserved for the loop back functionalities.