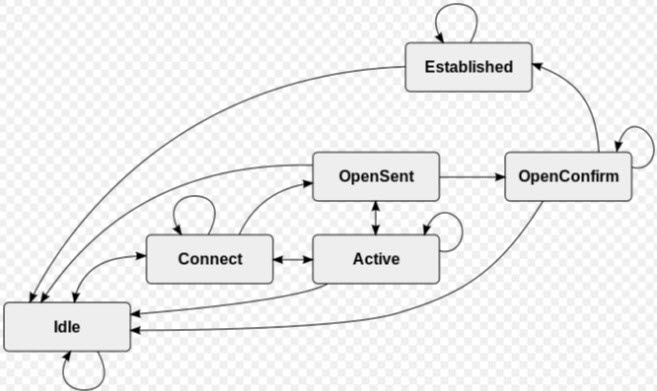
BGP Adjacency States
- Idle State
- Connect State
- Active State
- OpenSent State
- OpenConfirm State
- Established State
1. Idle State:
Idle is the initial state of a BGP connection. The BGP speaker is waiting for a start event, generally either the establishment of a TCP connection or the re-establishment of a previous connection. Once the connection is established, BGP moves to the next state.
Attributes
- Refuse all incoming BGP connections
- Start the initialization of event triggers
- Initiates a TCP connection with its configured BGP peer
- Listens for a TCP connection from its peer
- Changes its state to Connect
If an error occurs at any state of the FSM process, the BGP session is terminated immediately and returned to the Idle state. Some of the reasons why a router does not progress from the Idle state are:
- TCP port 179 is not open
- A random TCP port over 1023 is not open
- Peer address configured incorrectly on either router
- AS number configured incorrectly on either router
2. Connect State:
Connect is the next state of a BGP connection. If the TCP connection completes, BGP will move to the OpenSent stage if the connection does not complete, BGP goes to Active.
Attributes
- Waits for successful TCP negotiation with peer
- BGP does not spend much time in this state if the TCP session has been successfully established
- Sends Open message to peer and changes state to OpenSent
If an error occurs, BGP moves to the Active state. Some reasons for the error are:
- TCP port 179 is not open
- A random TCP port over 1023 is not open
- Peer address configured incorrectly on either router
- AS number configured incorrectly on either router
3. Active State:
Active indicates that the BGP speaker is continuing to create a peer relationship with the remote router. If this is successful, the BGP state goes to OpenSent. You’ll occasionally see a BGP connection flap between Active and Connect. This indicates an issue with the physical cable itself, or with the configuration.
Attributes
- If the router was unable to establish a successful TCP session, then it ends up in the Active state
- BGP FSM tries to restart another TCP session with the peer and, if successful, then it sends an Open message to the peer
- If it is unsuccessful again, the FSM is reset to the Idle state
Repeated failures may result in a router cycling between the Idle and Active states. Some of the reasons for this include:
- TCP port 179 is not open
- A random TCP port over 1023 is not open
- BGP configuration error
- Network congestion
- Flapping network interface
4. OpenSent State:
OpenSent indicates that the BGP speaker has received an Open message from the peer. BGP will determine whether the peer is in the same AS (iBGP) or a different AS (eBGP) in this state.
Attributes
- BGP FSM listens for an Open message from its peer
- Once the message has been received, the router checks the validity of the Open message
- If there is an error it is because one of the fields in the Open message doesn’t match between the peers, e.g., BGP version mismatch, MD5 password mismatch, the peering router expects a different My AS, etc. The router then sends a Notification message to the peer indicating why the error occurred
- If there is no error, a Keepalive message is sent, various timers are set and the state is changed to OpenConfirm
5. OpenConfirm State:
In OpenConfirm state, the BGP speaker is waiting for a keepalive message. If one is received, the state moves to Established, and the neighbor relationship is complete. It is in the Established state that update packets are actually exchanged.
Attributes
- The peer is listening for a Keepalive message from its peer
- If a Keepalive message is received and no timer has expired before reception of the Keepalive, BGP transitions to the Established state
- If a timer expires before a Keepalive message is received, or if an error condition occurs, the router transitions back to the Idle state
6. Established State:
In Established state, if one of keepalive message is received, the state moves to Established, and the neighbor relationship is complete. It is in the Established state that update packets are actually exchanged.
Attributes
- In this state, the peers send update messages to exchange information about each route being advertised to the BGP peer
- If there is any error in the update message then a Notification message is sent to the peer, and BGP transitions back to the idle state
- If a timer expires before a Keepalive message is received, or if an error condition occurs, the router transitions back to the Idle state